The Indian education system is an extensive network of schools, universities, and other institutions that cater to the educational needs of over 1.3 billion people. Education in India has come a long way, but it still faces many challenges, including poor infrastructure, lack of resources, and low literacy rates. In this article, we will discuss the role of the government in shaping the Indian education system and the impact of the New Education Policy (NEP) on the future of education in India.
The Current State of Education in India
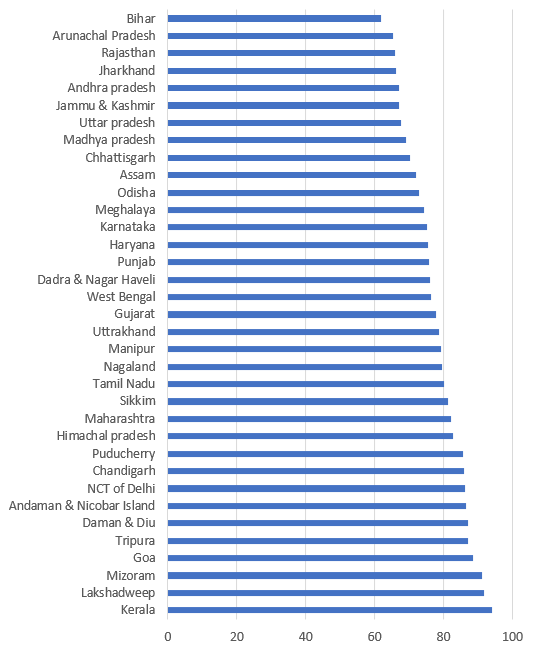
According to the latest data, India has a literacy rate of 74.04%, with significant disparities between urban and rural areas. While the literacy rate in urban areas is 86%, it drops to 71% in rural areas. This disparity is also reflected in the quality of education available in these areas. Rural schools often lack basic infrastructure, such as proper classrooms, toilets, and clean drinking water. Furthermore, the lack of qualified teachers in these areas means that many children do not receive a quality education.
Another significant challenge faced by the Indian education system is the lack of access to higher education. Only 26% of the Indian population has access to higher education, with many unable to afford the high fees charged by universities. This has led to a significant skills gap in the workforce, with many graduates lacking the skills required for the modern job market.
The Role of the Government in Shaping the Indian Education System
The Indian government has recognized the need for reform in the education system and has taken several steps to improve the quality of education. The government has launched several initiatives, such as the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) and the Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA), to improve access to education and infrastructure in rural areas. Additionally, the government has increased spending on education, with the education budget increasing from INR 1.32 trillion in 2018-19 to INR 1.5 trillion in 2019-20.
One of the most significant changes to the Indian education system came with the introduction of the New Education Policy (NEP) in 2020. The NEP aims to transform the education system in India and make it more relevant to the modern world. The NEP emphasizes the need for multidisciplinary education and the integration of vocational training into the mainstream curriculum. It also proposes changes to the assessment system, with a focus on skill-based evaluation rather than rote learning.
Impact of the New Education Policy (NEP) on the Future of Education in India
The NEP has the potential to revolutionize the Indian education system and prepare students for the challenges of the 21st century. By emphasizing the need for multidisciplinary education, the NEP aims to produce graduates who are equipped with a broad range of skills and knowledge. The integration of vocational training into the mainstream curriculum will also help to bridge the skills gap in the workforce and improve employability.
Furthermore, the changes to the assessment system proposed by the NEP will help to reduce the emphasis on rote learning and promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills. The NEP also proposes changes to teacher training, with a focus on continuous professional development and the use of technology in the classroom.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Indian education system has come a long way, but there is still much work to be done. The government plays a critical role in shaping the education system and has taken several steps to improve access to education and infrastructure in rural areas. The NEP represents a significant step forward in transforming the Indian education system and preparing students for the challenges of the 21st century. By emphasizing the need for multidisciplinary education, vocational training, skill-based evaluation, and teacher training, the NEP has the potential to revolutionize the education system in India.

